Improve
Overview¶
The improve tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically generates meaningful suggestions for improving the PR code.
The tool can be triggered automatically every time a new PR is opened, or it can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
How it looks¶
The following features are available only for Qodo Merge 💎 users:
- The
Apply / Chatcheckbox, which interactively converts a suggestion into a committable code comment - The
Morecheckbox to generate additional suggestions - On Bitbucket (Cloud & Data Center) and GitLab Server (v16 and earlier), you can invoke More Suggestions manually
Example usage¶
Manual triggering¶
Invoke the tool manually by commenting /improve on any PR. The code suggestions by default are presented as a single comment:
To edit configurations related to the improve tool, use the following template:
For example, you can choose to present all the suggestions as committable code comments, by running the following command:
Manual more suggestions¶
To generate more suggestions (distinct from the ones already generated), for git-providers that don't support interactive checkbox option, you can manually run:
Automatic triggering¶
To run the improve automatically when a PR is opened, define in a configuration file:
[github_app]
pr_commands = [
"/improve",
...
]
[pr_code_suggestions]
num_code_suggestions_per_chunk = ...
...
- The
pr_commandslists commands that will be executed automatically when a PR is opened. - The
[pr_code_suggestions]section contains the configurations for theimprovetool you want to edit (if any)
Table vs Committable code comments¶
Qodo Merge supports two modes for presenting code suggestions:
1) Table mode
2) Inline Committable code comments mode.
The table format offers several key advantages:
- Reduced noise: Creates a cleaner PR experience with less clutter
- Quick overview and prioritization: Enables quick review of one-liner summaries, impact levels, and easy prioritization
- High-level suggestions: High-level suggestions that aren't tied to specific code chunks are presented only in the table mode
- Interactive features: Provides 'more' and 'update' functionality via clickable buttons
- Centralized tracking: Shows suggestion implementation status in one place
- IDE integration: Allows applying suggestions directly in your IDE via Qodo Command
Table mode is the default of Qodo Merge, and is recommended approach for most users due to these benefits.
Teams with specific preferences can enable committable code comments mode in their local configuration, or use dual publishing mode.
Note - due to platform limitations, Bitbucket cloud and server supports only committable code comments mode.
Assessing Impact¶
💎 feature
Qodo Merge tracks two types of implementations for tracking implemented suggestions:
- Direct implementation - when the user directly applies the suggestion by clicking the
Applycheckbox. - Indirect implementation - when the user implements the suggestion in their IDE environment. In this case, Qodo Merge will utilize, after each commit, a dedicated logic to identify if a suggestion was implemented, and will mark it as implemented.
In post-process, Qodo Merge counts the number of suggestions that were implemented, and provides general statistics and insights about the suggestions' impact on the PR process.
Suggestion tracking¶
💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab
Qodo Merge employs a novel detection system to automatically identify AI code suggestions that PR authors have accepted and implemented.
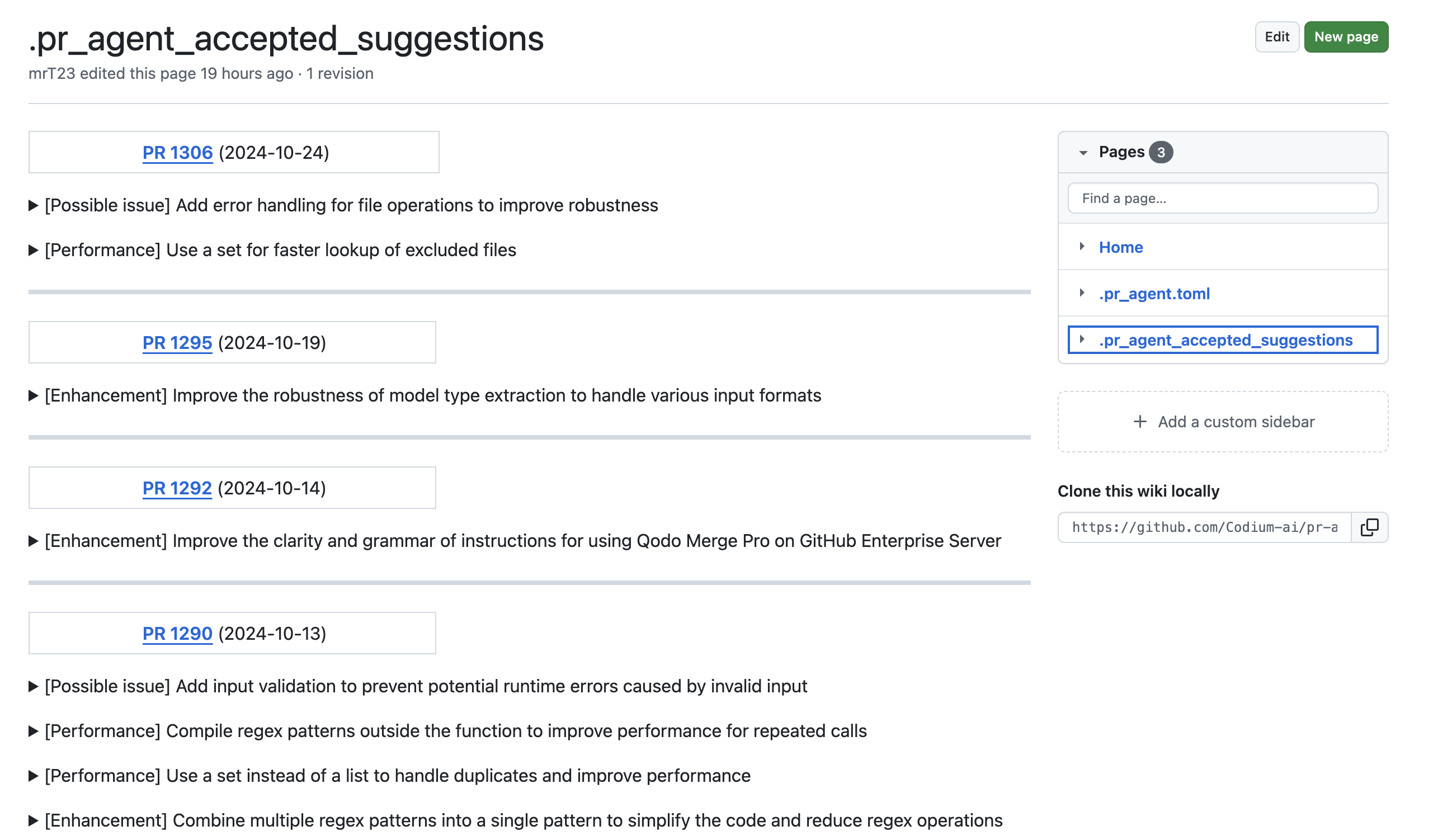
Accepted suggestions are also automatically documented in a dedicated wiki page called .pr_agent_accepted_suggestions, allowing users to track historical changes, assess the tool's effectiveness, and learn from previously implemented recommendations in the repository.
An example result:
This dedicated wiki page will also serve as a foundation for future AI model improvements, allowing it to learn from historically implemented suggestions and generate more targeted, contextually relevant recommendations.
This feature is controlled by a boolean configuration parameter: pr_code_suggestions.wiki_page_accepted_suggestions (default is true).
Wiki must be enabled
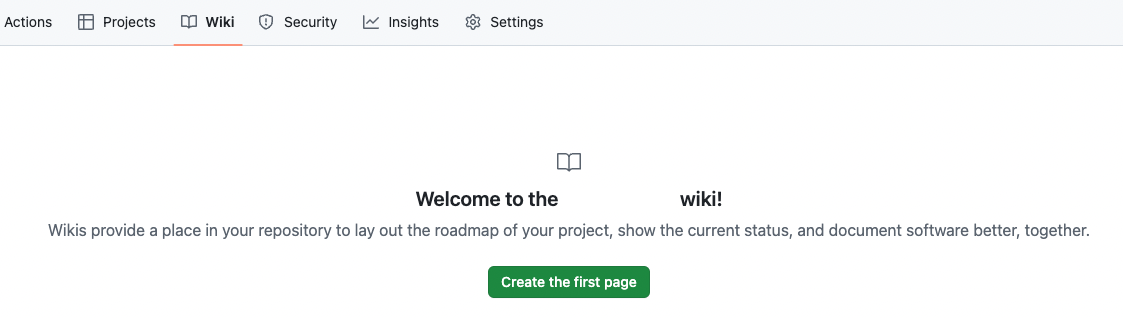
While the aggregation process is automatic, GitHub repositories require a one-time manual wiki setup.
To initialize the wiki: navigate to Wiki, select Create the first page, then click Save page.
Once a wiki repo is created, the tool will automatically use this wiki for tracking suggestions.
Why a wiki page?
Your code belongs to you, and we respect your privacy. Hence, we won't store any code suggestions in an external database.
Instead, we leverage a dedicated private page, within your repository wiki, to track suggestions. This approach offers convenient secure suggestion tracking while avoiding pull requests or any noise to the main repository.
Extra instructions and best practices¶
The improve tool can be further customized by providing additional instructions and best practices to the AI model.
Extra instructions¶
You can use the extra_instructions configuration option to give the AI model additional instructions for the improve tool.
Be specific, clear, and concise in the instructions. With extra instructions, you are the prompter.
Examples for possible instructions:
[pr_code_suggestions]
extra_instructions="""\
(1) Answer in Japanese
(2) Don't suggest to add try-except block
(3) Ignore changes in toml files
...
"""
Use triple quotes to write multi-line instructions. Use bullet points or numbers to make the instructions more readable.
Best practices¶
💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket
Qodo Merge supports both simple and hierarchical best practices configurations to provide guidance to the AI model for generating relevant code suggestions.
Writing effective best practices files
The following guidelines apply to all best practices files:
- Write clearly and concisely
- Include brief code examples when helpful with before/after patterns
- Focus on project-specific guidelines that will result in relevant suggestions you actually want to get
- Keep each file relatively short, under 800 lines, since:
- AI models may not process effectively very long documents
- Long files tend to contain generic guidelines already known to AI
- Maximum multiple file accumulated content is limited to 2000 lines.
- Use pattern-based structure rather than simple bullet points for better clarity
Example of a best practices file
Pattern 1: Add proper error handling with try-except blocks around external function calls.
Example code before:
Example code after:
try:
# Some code that might raise an exception
return process_pr_data(data)
except Exception as e:
logger.exception("Failed to process request", extra={"error": e})
Pattern 2: Add defensive null/empty checks before accessing object properties or performing operations on potentially null variables to prevent runtime errors.
Example code before:
def get_pr_code(pr_data):
if "changed_code" in pr_data:
return pr_data.get("changed_code", "")
return ""
Example code after:
Local best practices¶
For basic usage, create a best_practices.md file in your repository's root directory containing a list of best practices, coding standards, and guidelines specific to your repository.
The AI model will use this best_practices.md file as a reference, and in case the PR code violates any of the guidelines, it will create additional suggestions, with a dedicated label: Organization best practice.
Global hierarchical best practices¶
For organizations managing multiple repositories with different requirements, Qodo Merge supports a hierarchical best practices system using a dedicated global configuration repository.
Supported scenarios:
- Standalone repositories: Individual repositories can have their own specific best practices tailored to their unique requirements
- Groups of repositories: Repositories can be mapped to shared group-level best practices for consistent standards across similar projects
- Monorepos with subprojects: Large monorepos can have both repository-level and subproject-level best practices, with automatic path-based matching
Setting up global hierarchical best practices¶
1. Create a new repository named pr-agent-settings in your organization/workspace.
2. Build the folder hierarchy in your pr-agent-settings repository, for example:
pr-agent-settings/
├── metadata.yaml # Maps repos/folders to best practice paths
└── codebase_standards/ # Root for all best practice definitions
├── global/ # Global rules, inherited widely
│ └── best_practices.md
├── groups/ # For groups of repositories
│ ├── frontend_repos/
│ │ └── best_practices.md
│ ├── backend_repos/
│ │ └── best_practices.md
│ ├── python_repos/
│ │ └── best_practices.md
│ ├── cpp_repos/
│ │ └── best_practices.md
│ └── ...
├── repo_a/ # For standalone repositories
│ └── best_practices.md
├── monorepo-name/ # For monorepo-specific rules
│ ├── best_practices.md # Root level monorepo rules
│ ├── service-a/ # Subproject best practices
│ │ └── best_practices.md
│ └── service-b/ # Another subproject
│ └── best_practices.md
└── ... # More repositories
Note: In this structure,
pr-agent-settings,codebase_standards,global,groups,metadata.yaml, andbest_practices.mdare hardcoded names that must be used exactly as shown. All other names (such asfrontend_repos,backend_repos,repo_a,monorepo-name,service-a, etc.) are examples and should be replaced with your actual repository and service names.
Grouping and categorizing best practices
- Each folder (including the global folder) can contain a single
best_practices.mdfile - Organize repository best practices by creating subfolders within the
groupsfolder. Group them by purpose, programming languages, or other categories
3. Define the metadata file metadata.yaml that maps your repositories to their relevant best practices paths, for example:
# Standalone repos
repo_a:
best_practices_paths:
- "repo_a"
# Group-associated repos
repo_b:
best_practices_paths:
- "groups/backend_repos"
# Multi-group repos
repo_c:
best_practices_paths:
- "groups/frontend_repos"
- "groups/backend_repos"
# Monorepo with subprojects
monorepo-name:
best_practices_paths:
- "monorepo-name"
monorepo_subprojects:
service-a:
best_practices_paths:
- "monorepo-name/service-a"
service-b:
best_practices_paths:
- "monorepo-name/service-b"
4. Set the following configuration in your global configuration file:
Best practices priority and fallback behavior
When global best practices are enabled, Qodo Merge follows this priority order:
1. Primary: Global hierarchical best practices from pr-agent-settings repository:
1.1 If the repository is mapped in `metadata.yaml`, it uses the specified paths
1.2 For monorepos, it automatically collects best practices matching PR file paths
1.3 If no mapping exists, it falls back to the global best practices
2. Fallback: Local repository best_practices.md file:
2.1 Used when global best practices are not found or configured
2.2 Acts as a safety net for repositories not yet configured in the global system
2.3 Local best practices are completely ignored when global best practices are successfully loaded
Edge cases and behavior
- Missing paths: If specified paths in
metadata.yamldon't exist in the file system, those paths are skipped - Monorepo subproject matching: For monorepos, Qodo Merge automatically matches PR file paths against subproject paths to apply relevant best practices
- Multiple group inheritance: Repositories can inherit from multiple groups, and all applicable best practices are combined
Dedicated label for best practices suggestions
Best practice suggestions are labeled as Organization best practice by default.
To customize this label, modify it in your configuration file:
And the label will be: {organization_name} best practice.
Example results¶
Auto best practices¶
💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub.
Auto best practices is a novel Qodo Merge capability that:
- Identifies recurring patterns from accepted suggestions
- Automatically generates best practices page based on what your team consistently values
- Applies these learned patterns to future code reviews
This creates an automatic feedback loop where the system continuously learns from your team's choices to provide increasingly relevant suggestions. The system maintains two analysis phases:
- Open exploration for new issues
- Targeted checking against established best practices
Note that when a custom best practices exist, Qodo Merge will still generate an 'auto best practices' wiki file, though it won't use it in the improve tool.
Learn more about utilizing 'auto best practices' in our detailed guide.
Relevant configurations¶
[auto_best_practices]
# Disable all auto best practices usage or generation
enable_auto_best_practices = true
# Disable usage of auto best practices file in the 'improve' tool
utilize_auto_best_practices = true
# Extra instructions to the auto best practices generation prompt
extra_instructions = ""
# Max number of patterns to be detected
max_patterns = 5
Multiple best practices sources¶
The improve tool will combine best practices from all available sources - global configuration, local configuration, and auto-generated files - to provide you with comprehensive recommendations.
Combining 'extra instructions' and 'best practices'¶
💎 feature
The extra instructions configuration is more related to the improve tool prompt. It can be used, for example, to avoid specific suggestions ("Don't suggest to add try-except block", "Ignore changes in toml files", ...) or to emphasize specific aspects or formats ("Answer in Japanese", "Give only short suggestions", ...)
In contrast, the best_practices.md file is a general guideline for the way code should be written in the repo.
Using a combination of both can help the AI model to provide relevant and tailored suggestions.
Usage Tips¶
Implementing the proposed code suggestions¶
Each generated suggestion consists of three key elements:
- A single-line summary of the proposed change
- An expandable section containing a comprehensive description of the suggestion
- A diff snippet showing the recommended code modification (before and after)
We advise users to apply critical analysis and judgment when implementing the proposed suggestions. In addition to mistakes (which may happen, but are rare), sometimes the presented code modification may serve more as an illustrative example than a directly applicable solution. In such cases, we recommend prioritizing the suggestion's detailed description, using the diff snippet primarily as a supporting reference.
Dual publishing mode¶
Our recommended approach for presenting code suggestions is through a table (--pr_code_suggestions.commitable_code_suggestions=false).
This method significantly reduces the PR footprint and allows for quick and easy digestion of multiple suggestions.
We also offer a complementary dual publishing mode. When enabled, suggestions exceeding a certain score threshold are not only displayed in the table, but also presented as committable PR comments. This mode helps highlight suggestions deemed more critical.
To activate dual publishing mode, use the following setting:
Where x represents the minimum score threshold (>=) for suggestions to be presented as committable PR comments in addition to the table. Default is -1 (disabled).
Controlling suggestions depth¶
💎 feature
You can control the depth and comprehensiveness of the code suggestions by using the pr_code_suggestions.suggestions_depth parameter.
Available options:
selective- Shows only suggestions above a score threshold of 6regular- Default mode with balanced suggestion coverageexhaustive- Provides maximum suggestion comprehensiveness
(Alternatively, use numeric values: 1, 2, or 3 respectively)
We recommend starting with regular mode, then exploring exhaustive mode, which can provide more comprehensive suggestions and enhanced bug detection.
Self-review¶
💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab
If you set in a configuration file:
The improve tool will add a checkbox below the suggestions, prompting user to acknowledge that they have reviewed the suggestions.
You can set the content of the checkbox text via:
Tip - Reducing visual footprint after self-review 💎
The configuration parameter pr_code_suggestions.fold_suggestions_on_self_review (default is True)
can be used to automatically fold the suggestions after the user clicks the self-review checkbox.
This reduces the visual footprint of the suggestions, and also indicates to the PR reviewer that the suggestions have been reviewed by the PR author, and don't require further attention.
Tip - Demanding self-review from the PR author 💎
By setting:
the tool can automatically add an approval when the PR author clicks the self-review checkbox.- If you set the number of required reviewers for a PR to 2, this effectively means that the PR author must click the self-review checkbox before the PR can be merged (in addition to a human reviewer).
-
If you keep the number of required reviewers for a PR to 1 and enable this configuration, this effectively means that the PR author can approve the PR by actively clicking the self-review checkbox.
To prevent unauthorized approvals, this configuration defaults to false, and cannot be altered through online comments; enabling requires a direct update to the configuration file and a commit to the repository. This ensures that utilizing the feature demands a deliberate documented decision by the repository owner.
How many code suggestions are generated?¶
Qodo Merge uses a dynamic strategy to generate code suggestions based on the size of the pull request (PR). Here's how it works:
1. Chunking large PRs¶
- Qodo Merge divides large PRs into 'chunks'.
- Each chunk contains up to
config.max_model_tokenstokens (default: 32,000).
2. Generating suggestions¶
- For each chunk, Qodo Merge generates up to
pr_code_suggestions.num_code_suggestions_per_chunksuggestions (default: 3).
This approach has two main benefits:
- Scalability: The number of suggestions scales with the PR size, rather than being fixed.
- Quality: By processing smaller chunks, the AI can maintain higher quality suggestions, as larger contexts tend to decrease AI performance.
Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 lines of code), Qodo Merge will be able to process the entire code in a single call.
Maximum coverage configuration¶
💎 feature
For critical code reviews requiring maximum coverage, you can combine several settings to achieve a "super exhaustive" analysis. This is not a built-in mode, but a configuration recipe for advanced use cases.
# Recipe for maximum suggestion comprehensiveness
[pr_code_suggestions]
suggestions_depth = "exhaustive"
enable_suggestion_type_reuse = true
num_code_suggestions_per_chunk = 100
num_best_practice_suggestions = 100
This configuration is recommended for:
- Critical code reviews requiring maximum coverage
- Final reviews before major releases
- Code quality audits
Performance considerations
This configuration will significantly increase:
- Analysis time and API costs
- Number of suggestions generated (potentially overwhelming)
- Comment volume in your PR
Use this configuration judiciously and consider your team's review capacity.
Configuration options¶
General options
| extra_instructions | Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ...". |
| commitable_code_suggestions | If set to true, the tool will display the suggestions as committable code comments. Default is false. |
| enable_chat_in_code_suggestions | If set to true, QM bot will interact with comments made on code changes it has proposed. Default is true. |
| suggestions_depth 💎 | Controls the depth of the suggestions. Can be set to 'selective', 'regular', or 'exhaustive'. Default is 'regular'. |
| dual_publishing_score_threshold | Minimum score threshold for suggestions to be presented as committable PR comments in addition to the table. Default is -1 (disabled). |
| focus_only_on_problems | If set to true, suggestions will focus primarily on identifying and fixing code problems, and less on style considerations like best practices, maintainability, or readability. Default is true. |
| persistent_comment | If set to true, the improve comment will be persistent, meaning that every new improve request will edit the previous one. Default is true. |
| suggestions_score_threshold | Any suggestion with importance score less than this threshold will be removed. Default is 0. Highly recommend not to set this value above 7-8, since above it may clip relevant suggestions that can be useful. |
| apply_suggestions_checkbox | Enable the checkbox to create a committable suggestion. Default is true. |
| enable_more_suggestions_checkbox | Enable the checkbox to generate more suggestions. Default is true. |
| enable_help_text | If set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is false. |
| enable_chat_text | If set to true, the tool will display a reference to the PR chat in the comment. Default is false. |
| publish_output_no_suggestions | If set to true, the tool will publish a comment even if no suggestions were found. Default is true. |
| wiki_page_accepted_suggestions | If set to true, the tool will automatically track accepted suggestions in a dedicated wiki page called .pr_agent_accepted_suggestions. Default is true. |
| allow_thumbs_up_down | If set to true, all code suggestions will have thumbs up and thumbs down buttons, to encourage users to provide feedback on the suggestions. Default is false. Note that this feature is for statistics tracking. It will not affect future feedback from the AI model. |
Params for number of suggestions and AI calls
| auto_extended_mode | Enable chunking the PR code and running the tool on each chunk. Default is true. |
| num_code_suggestions_per_chunk | Number of code suggestions provided by the 'improve' tool, per chunk. Default is 3. |
| num_best_practice_suggestions 💎 | Number of code suggestions provided by the 'improve' tool for best practices. Default is 1. |
| max_number_of_calls | Maximum number of chunks. Default is 3. |
Understanding AI Code Suggestions¶
- AI Limitations: AI models for code are getting better and better, but they are not flawless. Not all the suggestions will be perfect, and a user should not accept all of them automatically. Critical reading and judgment are required. Mistakes of the AI are rare but can happen, and it is usually quite easy for a human to spot them.
- Purpose of Suggestions:
- Self-reflection: The suggestions aim to enable developers to self-reflect and improve their pull requests. This process can help to identify blind spots, uncover missed edge cases, and enhance code readability and coherency. Even when a specific code suggestion isn't suitable, the underlying issue it highlights often reveals something important that might deserve attention.
- Bug detection: The suggestions also alert on any critical bugs that may have been identified during the analysis. This provides an additional safety net to catch potential issues before they make it into production. It's perfectly acceptable to implement only the suggestions you find valuable for your specific context.
- Hierarchy: Presenting the suggestions in a structured hierarchical table enables the user to quickly understand them, and to decide which ones are relevant and which are not.
- Customization: To guide the model to suggestions that are more relevant to the specific needs of your project, we recommend using the
extra_instructionsandbest practicesfields. - Model Selection: SaaS users can also choose between different models. For specific programming languages or use cases, some models may perform better than others.
- Interactive usage: The interactive PR chat also provides an easy way to get more tailored suggestions and feedback from the AI model.